Your Haemoglobin dissociation curve animation images are ready in this website. Haemoglobin dissociation curve animation are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Haemoglobin dissociation curve animation files here. Get all free images.
If you’re searching for haemoglobin dissociation curve animation images information related to the haemoglobin dissociation curve animation interest, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always gives you hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Haemoglobin Dissociation Curve Animation. This is because haemoglobin has such a high affinity for oxygen; The reaction also causes the color of the rbcs in the vial to change from purple to red as shown in. A small change in the partial pressure of oxygen can have a very large impact on the percentage saturation of haemoglobin; In this the partial pressure of oxygen is on (x axis) and the.
 OxygenHemoglobin Dissociation Curve Mnemonic YouTube From youtube.com
OxygenHemoglobin Dissociation Curve Mnemonic YouTube From youtube.com
The curve can be shifted to the left or right by the factors listed. Most (97%) of the o2 binds to haemoglobin (hb) in the red blood cells, however a small amount (3%) dissolves in the plasma. The delivery of oxygen to tissues during acute anemia may be maintained by several compensatory mechanisms: Only the sigmoidal curve is characteristic of the cooperative process by which the release of one oxygen molecule alters the affinity for the remaining oxygens bound to the other. By union of the two curves you obtain the sigmoid. At lower oxygen tension, the slope of the oxygen dissociation curve is steeper.
The dissociation curve shifts to the right.
At lower oxygen tension, the slope of the oxygen dissociation curve is steeper. This is because haemoglobin has such a high affinity for oxygen; At lower oxygen tension, the slope of the oxygen dissociation curve is steeper. Oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve 5. The normal curve for adult haemoglobin is shown in red, with dots showing the normal values in arterial and venous blood. However, this relationship and the shape of the curve are not constant, as the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen is affected by the physiological environment.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
At higher oxygen tension, for example during pulmonary circulation, the oxygen dissociation curve plateaus. This graph shows how changes in the partial pressure of oxygen (po2) influence oxygen (o 2) binding to, and dissociation from, hemoglobin (hb). Only the sigmoidal curve is characteristic of the cooperative process by which the release of one oxygen molecule alters the affinity for the remaining oxygens bound to the other. Most (97%) of the o2 binds to haemoglobin (hb) in the red blood cells, however a small amount (3%) dissolves in the plasma. Explaining the oxygen dissociation curve.
 Source: what-when-how.com
Source: what-when-how.com
The curve shifts to the right. The normal curve for adult haemoglobin is shown in red, with dots showing the normal values in arterial and venous blood. Explaining the oxygen dissociation curve. This graph shows how changes in the partial pressure of oxygen (po2) influence oxygen (o 2) binding to, and dissociation from, hemoglobin (hb). The partial pressure of oxygen in the lungs is high, so haemoglobin picks up oxygen rapidly
 Source: thembbs.blogspot.com
Source: thembbs.blogspot.com
Most (97%) of the o2 binds to haemoglobin (hb) in the red blood cells, however a small amount (3%) dissolves in the plasma. This is because haemoglobin has such a high affinity for oxygen; This graph shows how changes in the partial pressure of oxygen (po2) influence oxygen (o 2) binding to, and dissociation from, hemoglobin (hb). At lower oxygen tension, the slope of the oxygen dissociation curve is steeper. Most (97%) of the o2 binds to haemoglobin (hb) in the red blood cells, however a small amount (3%) dissolves in the plasma.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The delivery of oxygen to tissues during acute anemia may be maintained by several compensatory mechanisms: Remember that the curve furthest to the left represents. The reaction also causes the color of the rbcs in the vial to change from purple to red as shown in. Oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve 5. The curve shifts to the right.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Explaining the oxygen dissociation curve. P 50, the p o 2 at which haemoglobin is 50% saturated, is indicated by the arrow showing a normal value of 3.5 kpa. At lower oxygen tension, the slope of the oxygen dissociation curve is steeper. This curve is an important tool for understanding how our blood carries and. The normal curve for adult haemoglobin is shown in red, with dots showing the normal values in arterial and venous blood.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The curve can be shifted to the left or right by the factors listed. The normal curve for adult haemoglobin is shown in red, with dots showing the normal values in arterial and venous blood. A small change in the partial pressure of oxygen can have a very large impact on the percentage saturation of haemoglobin; Explaining the oxygen dissociation curve. A small change in the partial pressure of oxygen can have a very large impact on the percentage saturation of haemoglobin;
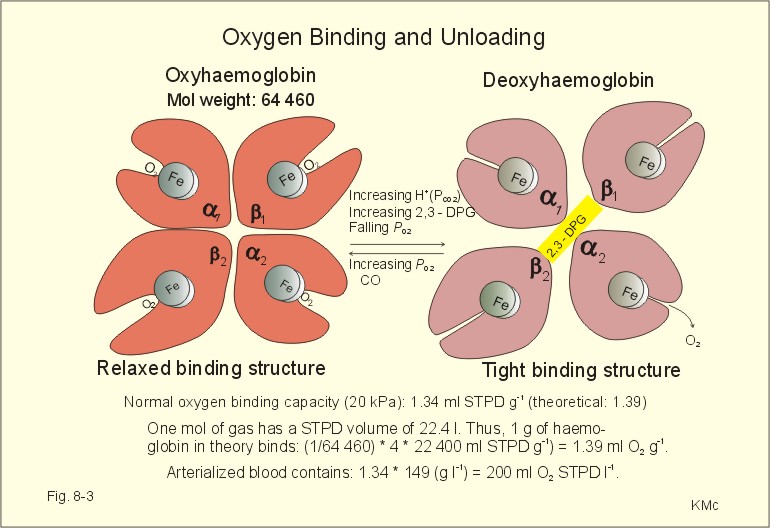 Source: lookfordiagnosis.com
Source: lookfordiagnosis.com
This is because haemoglobin has such a high affinity for oxygen; By union of the two curves you obtain the sigmoid. The curve shifts to the right. Explaining the oxygen dissociation curve. The dissociation curve shifts to the right.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title haemoglobin dissociation curve animation by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





